

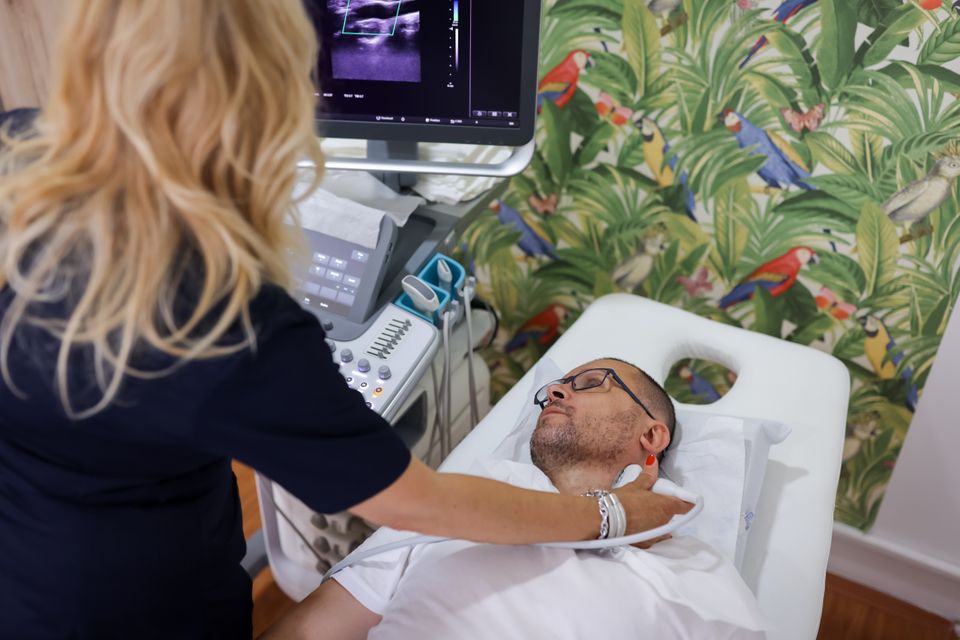
Cerebral Vascular Ultrasound
A Cerebral Vascular Ultrasound, commonly referred to as a Carotid Ultrasound, is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the carotid arteries located in the neck. These arteries are responsible for supplying blood to the brain, and the ultrasound helps assess their health and detect any narrowing (stenosis) or blockages that could lead to serious conditions like stroke.
Why the Exam Is Ordered:
This test is typically ordered to evaluate the risk of stroke or other cerebrovascular diseases. It may be recommended by your healthcare provider if you have risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including:
Symptoms That May Lead to an Ultrasound:
You may be referred for a carotid ultrasound if you are experiencing symptoms that suggest a potential issue with blood flow to the brain, such as:
To ensure accurate results, please follow these guidelines before your carotid ultrasound:
If you have any additional questions or concerns, our expert registered sonography team at PRECISION IMAGING LLC is here to help ensure you have a smooth, comfortable experience.
Why the Exam Is Ordered:
This test is typically ordered to evaluate the risk of stroke or other cerebrovascular diseases. It may be recommended by your healthcare provider if you have risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including:
- History of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- A family history of stroke or cardiovascular disease
Symptoms That May Lead to an Ultrasound:
You may be referred for a carotid ultrasound if you are experiencing symptoms that suggest a potential issue with blood flow to the brain, such as:
- Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision problems in one or both eyes
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Severe headache with no known cause
To ensure accurate results, please follow these guidelines before your carotid ultrasound:
- Avoid eating a heavy meal before the exam, as lying flat can cause discomfort.
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing with an open collar or neckline to provide access to the neck area.
- Remove any jewelry or accessories from the neck region.
- No special fasting or sedation is required for this exam.
If you have any additional questions or concerns, our expert registered sonography team at PRECISION IMAGING LLC is here to help ensure you have a smooth, comfortable experience.
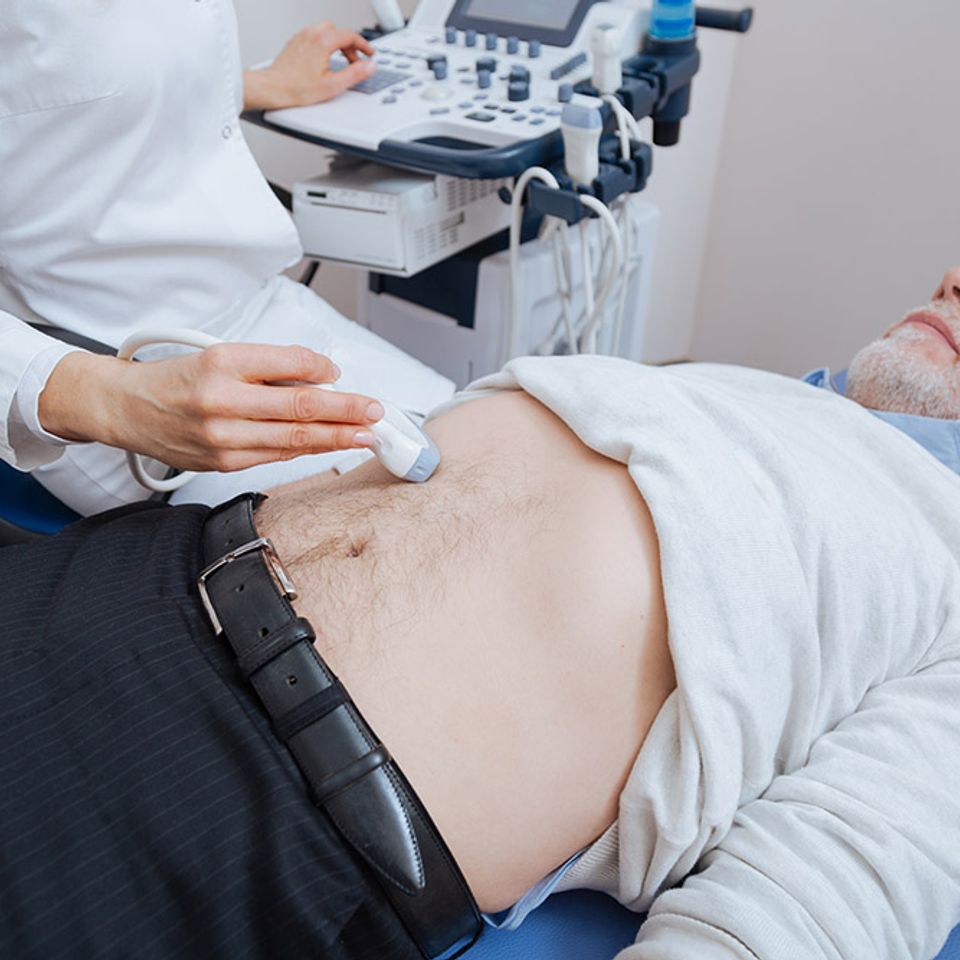
Aortic Vascular Ultrasound
An aortic vascular ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging exam that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. This exam helps to evaluate the health of the aorta, ensuring that it is functioning correctly and free from abnormalities such as aneurysms or blockages. The aortic ultrasound is particularly useful for identifying issues that may not present obvious symptoms until they become severe.
Why an Aortic Ultrasound is Ordered
Your doctor may recommend an aortic ultrasound for several reasons, including:
Some symptoms or risk factors may indicate a need for this ultrasound, such as:
Preparation for an aortic ultrasound is simple. To ensure accurate imaging, please follow these steps:
Why an Aortic Ultrasound is Ordered
Your doctor may recommend an aortic ultrasound for several reasons, including:
- Suspected or known abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), which is a dangerous bulging of the aorta.
- Screening for aneurysms, especially if you are over 65 or have a family history of aneurysms.
- Symptoms of potential arterial issues, such as sudden back or abdominal pain, feeling a pulsating sensation near the abdomen, or experiencing unexplained weight loss.
- High blood pressure or other risk factors for vascular disease.
Some symptoms or risk factors may indicate a need for this ultrasound, such as:
- Back or abdominal pain, especially if it is severe or unusual.
- A pulsating feeling in the abdomen, which could indicate a possible aneurysm.
- Family history of aortic aneurysms.
- Unexplained chest pain, nausea, or a feeling of lightheadedness, which may sometimes suggest vascular issues.
- High blood pressure, smoking, or other vascular disease risk factors.
Preparation for an aortic ultrasound is simple. To ensure accurate imaging, please follow these steps:
- Avoid eating or drinking for 6-8 hours prior to your appointment, as a full stomach can obscure the aorta.
- Take any medications as directed, unless your doctor advises otherwise.
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing, as you may need to adjust it for easy access to your abdominal area.
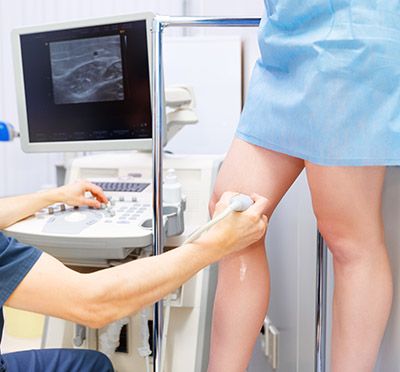
Venous Arms & Legs Ultrasound
A Venous Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the veins in your arms (upper extremities) or legs (lower extremities). The purpose of this exam is to evaluate the blood flow through your veins, primarily checking for the presence of blood clots (deep vein thrombosis, DVT) or other conditions like venous insufficiency, where blood doesn't flow properly back to the heart.
Why is the Exam Ordered?
Your healthcare provider may order a venous ultrasound if you are experiencing symptoms that could suggest a problem with your veins. Some common reasons for ordering this exam include:
Common Symptoms Leading to This Exam
Patients who are typically recommended for a venous ultrasound may experience the following symptoms:
A venous ultrasound is painless and typically takes 30–60 minutes. The sonographer will apply a warm gel to the skin over the area being examined and use a small device called a transducer. The transducer sends sound waves into the body, and images of the veins will appear on a screen. You may be asked to change positions, hold your breath, or bear down briefly to help assess how blood flows through the veins.
How to Prepare for the Exam
Why is the Exam Ordered?
Your healthcare provider may order a venous ultrasound if you are experiencing symptoms that could suggest a problem with your veins. Some common reasons for ordering this exam include:
- Suspected Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A serious condition where a blood clot forms in the deep veins of your legs or arms.
- Venous Insufficiency: A condition where the veins are unable to efficiently return blood from the limbs back to the heart, leading to swelling or varicose veins.
- Swelling in the Limbs: Unexplained swelling in your legs or arms may indicate a problem with venous blood flow.
- Pain in the Limbs: Sudden or persistent pain, especially if associated with swelling, may require an evaluation of the veins.
- Varicose Veins: Enlarged or twisted veins visible under the skin, often accompanied by discomfort or pain.
- Elevated D-Dimer Test: looks for D-dimer in blood. D-dimer is a protein fragment (small piece) that's made when a blood clot dissolves in your body. D-dimer isn't usually found in your blood unless your body is making or breaking up blood clots.
Common Symptoms Leading to This Exam
Patients who are typically recommended for a venous ultrasound may experience the following symptoms:
- Leg or Arm Pain: Sharp, throbbing, or aching pain in the extremities.
- Swelling in the Arms or Legs: Particularly if one limb is more swollen than the other.
- Redness or Warmth: A limb that feels warmer than usual or appears red could be a sign of a clot.
- Heaviness or Fatigue in the Legs: A sensation of heaviness or tiredness in the legs, especially after standing for long periods.
- Visible Varicose Veins: Large, twisted veins that are visible through the skin.
A venous ultrasound is painless and typically takes 30–60 minutes. The sonographer will apply a warm gel to the skin over the area being examined and use a small device called a transducer. The transducer sends sound waves into the body, and images of the veins will appear on a screen. You may be asked to change positions, hold your breath, or bear down briefly to help assess how blood flows through the veins.
How to Prepare for the Exam
- No Special Preparation Needed: There is no need for fasting or medication adjustments unless instructed otherwise by your healthcare provider.
- Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may be asked to wear a gown or remove clothing over the area to be examined (legs or arms).
- Medications: You can continue to take any prescribed medications unless your doctor has given you specific instructions.
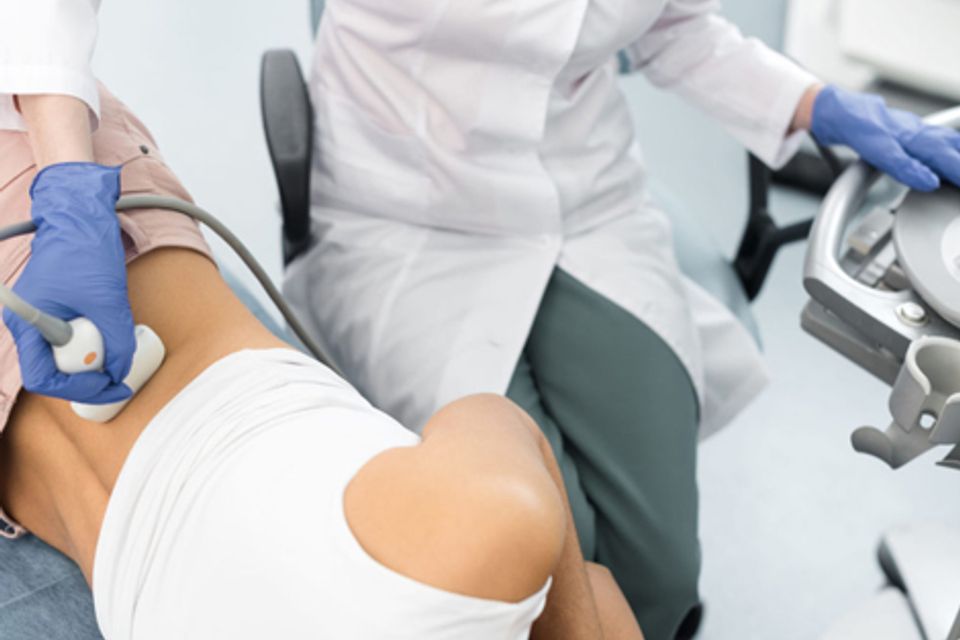

Renal Arterial Vascular Ultrasound
A renal arterial vascular ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging exam used to assess the blood flow in the arteries leading to the kidneys. This test helps evaluate the renal arteries for any blockages or narrowing (stenosis), which could reduce blood flow to the kidneys. Decreased blood flow to the kidneys can impact kidney function and may contribute to hypertension (high blood pressure) and other cardiovascular complications.
Why the Exam is Ordered
A physician may recommend a renal arterial ultrasound if you have symptoms or risk factors associated with renal artery disease. Common reasons for ordering this exam include:
Proper preparation ensures the accuracy of the exam and helps produce clear images:
Fasting: You may be asked to fast for about 6-8 hours before the exam. Avoiding food can reduce gas in the abdomen, allowing clearer views of the arteries. Hydration: You may need to drink water prior to the exam but avoid coffee, tea, or other caffeinated drinks. Medications: Continue your usual medications unless instructed otherwise by your physician.
During the procedure, a technician will use an ultrasound transducer over the abdomen to capture images of your renal arteries. The test typically takes 30-60 minutes, and you will be able to return to normal activities immediately afterward.
Why the Exam is Ordered
A physician may recommend a renal arterial ultrasound if you have symptoms or risk factors associated with renal artery disease. Common reasons for ordering this exam include:
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure, especially if resistant to medication
- Sudden or unexplained rise in blood pressure, particularly in younger adults or people over 50
- Reduced kidney function or signs of chronic kidney disease
- Fluid retention or swelling
- Decreased urine output
- Family history of renal artery stenosis or cardiovascular disease
Proper preparation ensures the accuracy of the exam and helps produce clear images:
Fasting: You may be asked to fast for about 6-8 hours before the exam. Avoiding food can reduce gas in the abdomen, allowing clearer views of the arteries. Hydration: You may need to drink water prior to the exam but avoid coffee, tea, or other caffeinated drinks. Medications: Continue your usual medications unless instructed otherwise by your physician.
During the procedure, a technician will use an ultrasound transducer over the abdomen to capture images of your renal arteries. The test typically takes 30-60 minutes, and you will be able to return to normal activities immediately afterward.
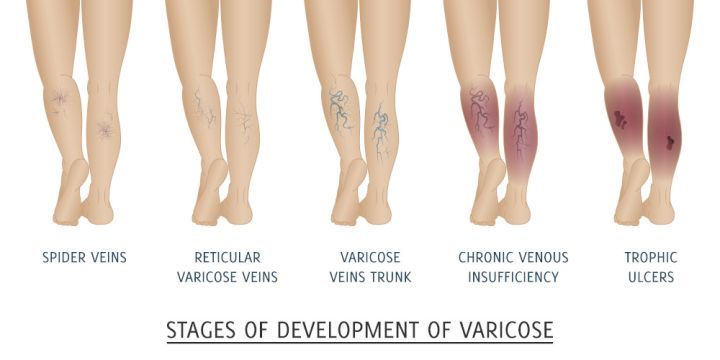
Venous Insufficiency Ultrasound
Exam Description: A venous insufficiency ultrasound is a specialized, non-invasive imaging exam that evaluates blood flow in the veins of the legs, primarily focusing on the valves and vein structure to identify issues with venous insufficiency. Venous insufficiency occurs when veins struggle to return blood from the legs back to the heart due to faulty valves, causing blood to pool or flow backward in the veins. This ultrasound helps to assess the health of these veins, detect blood clots (DVT), and measure the extent of valve damage or obstruction.
Why Is This Exam Ordered? Your healthcare provider may recommend a venous insufficiency ultrasound if you exhibit symptoms of venous insufficiency, which can include:
Patient Preparation:
Why Is This Exam Ordered? Your healthcare provider may recommend a venous insufficiency ultrasound if you exhibit symptoms of venous insufficiency, which can include:
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Pain or discomfort that worsens after standing or sitting for long periods
- Varicose or spider veins
- Leg heaviness or fatigue
- Skin discoloration or ulcers near the ankles
- A sensation of throbbing, cramping, or aching in the legs
Patient Preparation:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water before the exam to promote accurate imaging.
- Clothing: Wear loose-fitting, comfortable clothing that allows easy access to your legs, as the sonographer will need to scan both upper and lower leg areas.
- Avoid Lotions or Oils: Refrain from applying lotions, oils, or moisturizers on your legs on the day of the exam to prevent interference with the ultrasound probe and gel.
- Duration: Expect the exam to take about 30-45 minutes, during which you may be asked to change positions or briefly hold your breath to capture clearer images of the veins.
Arterial (arms and legs)
What is a Lower and Upper Extremity Arterial Ultrasound? A lower and upper extremity arterial ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to evaluate the blood flow in the arteries of the arms (upper extremities) and legs (lower extremities). It uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the arteries, helping to assess if there are any blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities in the blood vessels. This test is also known as arterial Doppler ultrasound.
Why is the Exam Ordered? This exam is typically ordered when there is suspicion of poor blood circulation in the arteries of the arms or legs. Conditions such as Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), arterial blockages, aneurysms, or blood clots may prompt your physician to recommend this ultrasound. Early detection of arterial problems can prevent serious complications, including limb loss in severe cases. Additionally, this can be ordered to look at bypass grafts, popliteal entrapment syndrome or pseudoaneurysm check after a catheterization.
Symptoms That May Lead to This Exam:
How to Prepare for the Exam:
If you have any questions or need further clarification, please feel free to ask your healthcare provider or contact PRECISION IMAGING LLC for more information.
Why is the Exam Ordered? This exam is typically ordered when there is suspicion of poor blood circulation in the arteries of the arms or legs. Conditions such as Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), arterial blockages, aneurysms, or blood clots may prompt your physician to recommend this ultrasound. Early detection of arterial problems can prevent serious complications, including limb loss in severe cases. Additionally, this can be ordered to look at bypass grafts, popliteal entrapment syndrome or pseudoaneurysm check after a catheterization.
Symptoms That May Lead to This Exam:
- Pain or cramping in the legs or arms during exercise (claudication)
- Coldness in the lower leg, foot, or arm, especially compared to the opposite side
- Non-healing wounds or ulcers on the legs, feet, or arms
- Numbness, weakness, or tingling in the extremities
- Changes in the color of the skin, such as turning pale, blue, or reddish
- Reduced hair growth on legs
- Decreased pulses in the feet or wrists
How to Prepare for the Exam:
- Wear loose-fitting, comfortable clothing. You may be asked to change into a gown for easier access to your arms and legs.
- Avoid applying lotion or oils to your arms and legs on the day of the exam, as it can interfere with the ultrasound results.
- No fasting is required, and you can take your medications as prescribed unless your doctor provides other instructions.
If you have any questions or need further clarification, please feel free to ask your healthcare provider or contact PRECISION IMAGING LLC for more information.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
This test would include an upper arterial study with a more in depth evaluation using specific movements of each arm to evaluate changes in the blood flow to the finger.
No preparations are necessary but you might need to remove your shirt.
No preparations are necessary but you might need to remove your shirt.
Mesenteric Vascular Ultrasound
A mesenteric vascular ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to evaluate blood flow through the major arteries that supply blood to your intestines, including the superior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric artery, and celiac artery. This exam helps in assessing the health of these vessels and identifying any narrowing or blockages that may impair blood flow.
Why This Exam is Ordered:
Your doctor may order a mesenteric vascular ultrasound if you are experiencing symptoms related to reduced blood flow in the abdominal organs. Common symptoms include:
Preparation for the Exam:
To obtain the clearest images, follow these preparation steps:
Fasting: Avoid eating or drinking for at least 6-8 hours prior to your exam. This helps reduce gas and movement in the intestines, allowing for better visualization of the blood vessels. Medications: You may continue taking any necessary medications with a small sip of water, but consult your doctor if you have any questions about specific medications. Comfortable Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing for easy access to the abdominal area.
During the exam, a trained sonographer will apply gel to your abdomen and use an ultrasound probe to capture real-time images of your blood vessels. The procedure is safe, painless, and typically takes around 30-45 minutes. Your healthcare provider will review the results with you to discuss any findings or next steps in your care.
Why This Exam is Ordered:
Your doctor may order a mesenteric vascular ultrasound if you are experiencing symptoms related to reduced blood flow in the abdominal organs. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain, especially after eating (postprandial pain)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Abdominal bloating or discomfort
Preparation for the Exam:
To obtain the clearest images, follow these preparation steps:
Fasting: Avoid eating or drinking for at least 6-8 hours prior to your exam. This helps reduce gas and movement in the intestines, allowing for better visualization of the blood vessels. Medications: You may continue taking any necessary medications with a small sip of water, but consult your doctor if you have any questions about specific medications. Comfortable Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing for easy access to the abdominal area.
During the exam, a trained sonographer will apply gel to your abdomen and use an ultrasound probe to capture real-time images of your blood vessels. The procedure is safe, painless, and typically takes around 30-45 minutes. Your healthcare provider will review the results with you to discuss any findings or next steps in your care.
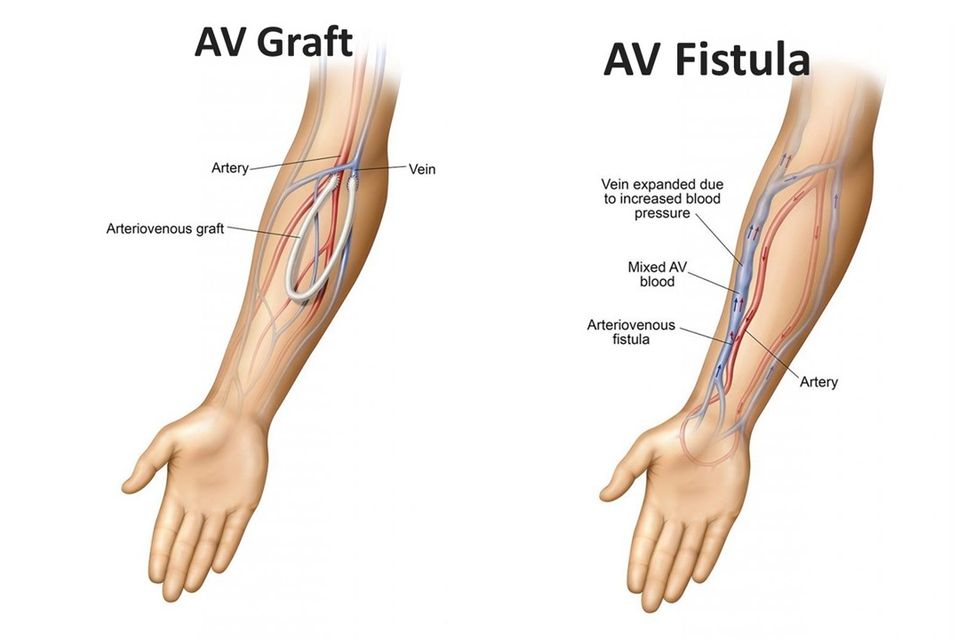
Dialysis Duplex Vascular Ultrasound
A Dialysis Duplex Vascular Ultrasound is a specialized imaging exam designed to assess blood flow within the dialysis access, typically an arteriovenous (AV) fistula or graft. The test uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images and evaluate the health of blood vessels in the access site, ensuring effective blood flow, which is essential for successful dialysis treatment.
Why This Exam Is Ordered
This exam is often recommended for patients with dialysis access to monitor the flow and detect any blockages, narrowing, or complications that may impair dialysis effectiveness. It can also be used for evaluating new AV fistulas or grafts to confirm that they are functioning as intended.
Common reasons for ordering a Dialysis Duplex Vascular Ultrasound include:
Patients may experience specific symptoms that indicate potential problems with their dialysis access. These may include:
Preparation Before the Exam
While no specific preparation is typically required for a Dialysis Duplex Vascular Ultrasound, it’s helpful to wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may be asked to remove any clothing or jewelry around the access site.
Why This Exam Is Ordered
This exam is often recommended for patients with dialysis access to monitor the flow and detect any blockages, narrowing, or complications that may impair dialysis effectiveness. It can also be used for evaluating new AV fistulas or grafts to confirm that they are functioning as intended.
Common reasons for ordering a Dialysis Duplex Vascular Ultrasound include:
- Monitoring for stenosis (narrowing) or clotting in an existing access
- Evaluating the maturation of a newly created AV fistula or graft
- Investigating symptoms of access failure or inadequate dialysis
Patients may experience specific symptoms that indicate potential problems with their dialysis access. These may include:
- Swelling in the arm near the access site
- Pain, tenderness, or redness around the access site
- Reduced or absent thrill (vibration) over the fistula or graft
- Difficulty with dialysis treatments or low blood flow during sessions
- Increased bleeding after dialysis needle removal
Preparation Before the Exam
While no specific preparation is typically required for a Dialysis Duplex Vascular Ultrasound, it’s helpful to wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may be asked to remove any clothing or jewelry around the access site.
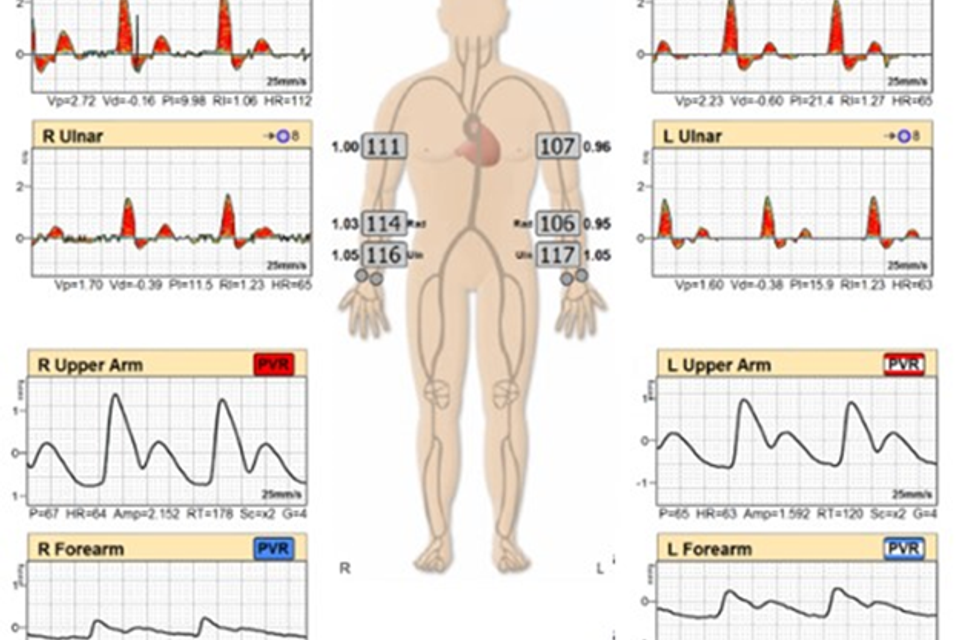
PVR/ABI
The Lower Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) and Upper Extremity Arterial Pulse Volume Recording (PVR) are non-invasive vascular tests used to evaluate blood flow in the arteries of the lower legs and arms. These exams help assess the presence of peripheral artery disease (PAD) by measuring the blood pressure and blood flow in the limbs, which can indicate narrowing or blockages in the arteries.
Your healthcare provider may order this exam if you show signs or symptoms of poor circulation, which can be caused by a variety of conditions, including:
Symptoms That May Lead to This Exam
You may be referred for an ABI and PVR test if you have symptoms such as:
For both the ABI and PVR exams, you will lie down on an exam table. Blood pressure cuffs will be placed around your arms, ankles, and sometimes other parts of your legs.
How to Prepare for the Exam
To ensure accurate results:
If you have any additional questions or concerns, our expert registered sonography team at PRECISION IMAGING LLC is here to help ensure you have a smooth, comfortable
- Lower ABI: This test compares the blood pressure in your lower legs to the blood pressure in your arms to determine if there is reduced blood flow to your legs, which is a common indicator of PAD.
- Upper Extremity Arterial PVR: This test measures the blood flow in your arms through a series of blood pressure cuffs and sensors that detect changes in the volume of blood flowing through the arteries.
Your healthcare provider may order this exam if you show signs or symptoms of poor circulation, which can be caused by a variety of conditions, including:
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): A condition where the arteries in your legs or arms become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, reducing blood flow.
- Raynaud’s Disease: A condition causing reduced blood flow to fingers and toes in response to cold or stress.
- Claudication: Pain or cramping in the legs or arms during exercise or movement, which usually goes away with rest, a key symptom of PAD.
- Cold or Numb Limbs: Experiencing coldness, numbness, or tingling in the legs or arms.
- Non-healing Wounds: Ulcers or wounds on the legs, feet, arms, or hands that are slow to heal.
Symptoms That May Lead to This Exam
You may be referred for an ABI and PVR test if you have symptoms such as:
- Leg pain, cramping, or heaviness during walking or exercise (claudication)
- Numbness or weakness in the legs or arms
- Coldness in your legs, feet, arms, or hands
- Sores or ulcers on your feet, toes, or fingers that are slow to heal
- A weak or absent pulse in your legs or arms
For both the ABI and PVR exams, you will lie down on an exam table. Blood pressure cuffs will be placed around your arms, ankles, and sometimes other parts of your legs.
- During the ABI, a handheld ultrasound device (Doppler) will be used to listen to the blood flow in your legs while the cuffs are inflated and deflated. The results will compare the blood pressure in your lower legs to that in your arms.
- During the PVR, cuffs are inflated to record pulse volume changes that occur with each heartbeat, showing how well blood is moving through the arteries.
How to Prepare for the Exam
To ensure accurate results:
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may need to remove shoes, socks, and possibly roll up your sleeves or pant legs.
- Avoid smoking or using tobacco products at least 2 hours before the exam, as this can constrict blood vessels and affect results.
- You may be asked to refrain from caffeine before the test, as it can also affect your blood vessels.
If you have any additional questions or concerns, our expert registered sonography team at PRECISION IMAGING LLC is here to help ensure you have a smooth, comfortable
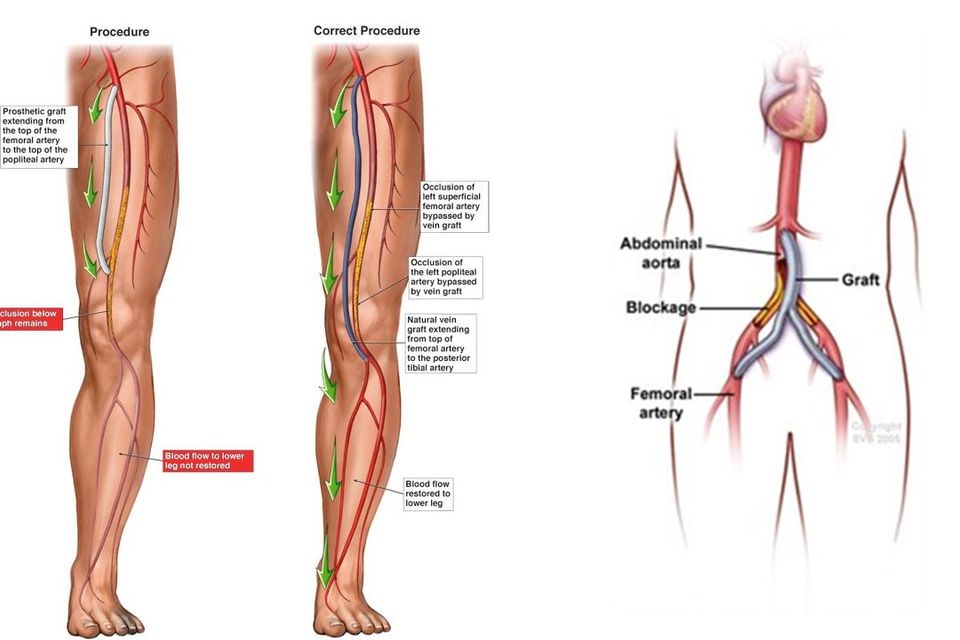
Bypass Graft Duplex Vascular Ultrasound
What is a Lower Extremity Bypass Graft Duplex Vascular Ultrasound?
A Lower Extremity Bypass Graft Duplex Ultrasound is a specialized imaging test that evaluates blood flow through a surgically placed bypass graft in the lower extremities (legs). This test uses sound waves to produce detailed images of the graft and surrounding blood vessels, allowing healthcare providers to monitor the graft's function and detect any potential complications, such as blockages, narrowing (stenosis), or other issues that may impair blood flow.
Why is this Exam Ordered?
This exam is typically ordered for patients who have undergone bypass surgery for blocked or narrowed arteries in the legs. A bypass graft is often necessary when the lower extremity arteries become narrowed or blocked, leading to reduced blood flow and insufficient oxygen supply to leg tissues. Reasons for ordering this exam may include:
A bypass graft may be required when a patient has symptoms of peripheral artery disease (PAD), which can include:
A Lower Extremity Bypass Graft Duplex Ultrasound is a specialized imaging test that evaluates blood flow through a surgically placed bypass graft in the lower extremities (legs). This test uses sound waves to produce detailed images of the graft and surrounding blood vessels, allowing healthcare providers to monitor the graft's function and detect any potential complications, such as blockages, narrowing (stenosis), or other issues that may impair blood flow.
Why is this Exam Ordered?
This exam is typically ordered for patients who have undergone bypass surgery for blocked or narrowed arteries in the legs. A bypass graft is often necessary when the lower extremity arteries become narrowed or blocked, leading to reduced blood flow and insufficient oxygen supply to leg tissues. Reasons for ordering this exam may include:
- Routine monitoring of the graft’s patency (openness) after surgery.
- Evaluation of new symptoms, such as pain or cramping in the legs, which may indicate graft complications.
- Assessment of blood flow in cases of suspected graft failure or decreased circulation in the leg.
A bypass graft may be required when a patient has symptoms of peripheral artery disease (PAD), which can include:
- Persistent pain or cramping in the legs, especially when walking or exercising (claudication).
- Pain at rest, especially in the toes or feet.
- Non-healing wounds or ulcers on the lower legs or feet.
- Coldness, numbness, or weakness in the legs or feet.
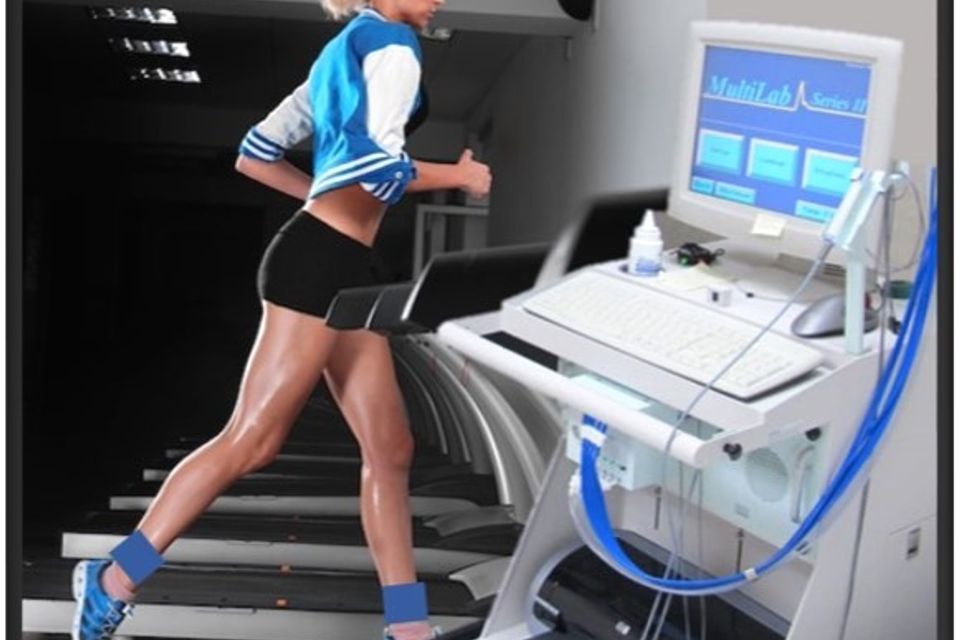

ABI/PVR with Exercise
What is an ABI/PVR with Exercise?
An Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) and Pulse Volume Recording (PVR) with exercise are non-invasive diagnostic tests used to assess the blood flow in the lower extremities. These tests are designed to evaluate for peripheral arterial disease (PAD), particularly in cases where symptoms occur during physical activity and are not evident at rest. ABI measures the blood pressure in the ankles and compares it to the blood pressure in the arms, while PVR evaluates blood flow through the arteries by analyzing waveform patterns.
When combined with exercise, these tests help identify blood flow limitations caused by arterial blockages that may only appear during activity, mimicking the stress experienced during walking or other forms of exertion.
The exam usually takes about 45–60 minutes. After the study, the results will be reviewed by your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate course of action.
If you have additional questions about the test or how to prepare, please contact PRECISION IMAGING LLC or your healthcare provider.
An Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) and Pulse Volume Recording (PVR) with exercise are non-invasive diagnostic tests used to assess the blood flow in the lower extremities. These tests are designed to evaluate for peripheral arterial disease (PAD), particularly in cases where symptoms occur during physical activity and are not evident at rest. ABI measures the blood pressure in the ankles and compares it to the blood pressure in the arms, while PVR evaluates blood flow through the arteries by analyzing waveform patterns.
When combined with exercise, these tests help identify blood flow limitations caused by arterial blockages that may only appear during activity, mimicking the stress experienced during walking or other forms of exertion.
Why Would This Exam Be Ordered?
Your physician may recommend an ABI/PVR with exercise if there is a suspicion of PAD or another vascular condition affecting the lower extremities. These tests help: Detect early stages of PAD or intermittent claudication (pain with walking). Assess the severity of blood flow restriction in the legs. Evaluate the need for further intervention, such as medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery. Monitor the progression of known arterial disease or the effectiveness of treatment.Symptoms Indicating the Need for ABI/PVR with Exercise
Patients with the following symptoms may benefit from this study:- Pain, cramping, or heaviness in the legs or buttocks during walking or exercise (intermittent claudication).
- Non-healing wounds or ulcers on the feet or legs.
- Coldness, numbness, or weakness in the lower extremities.
- A change in the color or temperature of the skin on the legs.
- Decreased hair growth or shiny skin on the legs.
- Rest pain in the feet or legs that improves when legs are elevated.
Patient Preparation
To ensure accurate results, please follow these preparation guidelines: Avoid Smoking: Refrain from smoking or using nicotine products for at least 4 hours before the exam, as nicotine can affect blood flow. Fasting: You may eat a light meal before the test, but avoid caffeine or heavy meals for at least 2 hours prior. Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing, such as shorts or easily removable pants, as the technician will need access to your legs and arms. Medications: Continue taking prescribed medications unless instructed otherwise by your physician. Activity Restrictions: Avoid strenuous exercise on the day of the exam before testing.What to Expect During the Exam
The test typically involves: Resting ABI/PVR: Blood pressure cuffs will be placed on your arms and legs to record baseline measurements of blood flow. Exercise Component: You will walk on a treadmill at a controlled speed and incline to replicate symptoms. If unable to walk, alternative methods may be used. Post-Exercise Measurements: Blood pressure and waveforms will be recorded immediately after exercise to assess changes in blood flow.The exam usually takes about 45–60 minutes. After the study, the results will be reviewed by your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate course of action.
If you have additional questions about the test or how to prepare, please contact PRECISION IMAGING LLC or your healthcare provider.
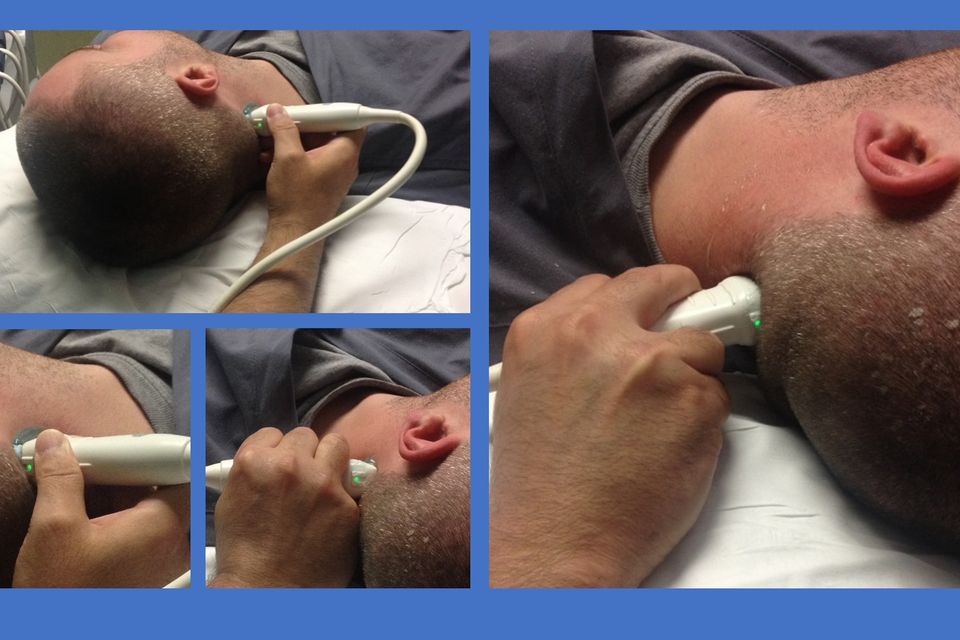
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) Ultrasound Examination
Description:
A Transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic test that evaluates blood flow in the major arteries of the brain. This exam uses high-frequency sound waves to measure the speed and direction of blood flow through the brain’s blood vessels, providing crucial information about cerebral circulation. It is safe, painless, and typically performed in an outpatient setting.
If you have questions or need more information about Transcranial Doppler ultrasound, feel free to contact PRECISION IMAGING LLC.
A Transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic test that evaluates blood flow in the major arteries of the brain. This exam uses high-frequency sound waves to measure the speed and direction of blood flow through the brain’s blood vessels, providing crucial information about cerebral circulation. It is safe, painless, and typically performed in an outpatient setting.
Why is a TCD Exam Ordered?
A TCD is often ordered to assess or monitor conditions affecting blood flow to the brain. Common reasons for ordering the test include:- Stroke or TIA Evaluation: To determine if reduced blood flow contributed to a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
- Sickle Cell Disease: To screen for stroke risk in children with sickle cell anemia.
- Cerebral Vasospasm: To monitor narrowing of blood vessels following a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Carotid Artery Disease: To assess how carotid artery narrowing impacts brain circulation.
- Brain Death Assessment: To confirm cessation of cerebral blood flow in suspected brain death.
- Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO): To evaluate for microembolic signals when performing a bubble study.
- Intracranial Stenosis: To detect and monitor narrowing of the arteries within the brain.
- Post-Procedure Monitoring: To assess the effectiveness of treatments such as angioplasty or thrombolysis.
Symptoms that May Require a TCD Ultrasound
- Sudden weakness or numbness, especially on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision changes or sudden loss of vision
- Severe, sudden-onset headaches
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Persistent symptoms of sickle cell anemia
- Symptoms of vasospasm, such as worsening neurological deficits after a brain bleed
Patient Preparation for the Study
- Clothing: Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. No need to undress as the test focuses on the head and neck.
- Avoid Caffeine and Nicotine: Refrain from consuming caffeine or smoking at least 2–4 hours prior to the test, as these can affect blood vessel constriction.
- Medication: Take your regular medications unless instructed otherwise by your physician.
- Bubble Study (if needed): If the test includes a bubble study to evaluate for PFO, you may be asked to drink extra fluids beforehand.
If you have questions or need more information about Transcranial Doppler ultrasound, feel free to contact PRECISION IMAGING LLC.

